While multicellular organisms contain multiple cells, single-celled, or unicellular organisms, just have one organism to make up their being.
Single Cell Organisms
As implied in their name, single cell organisms depend on just one cell for them to carry out all necessary functions. These organisms include yeast, bacteria, and protists.
The biggest single cell organisms may be classified as eukaryotes or prokaryotes. Eukaryotes have a membrane-bound nucleus that holds genetic material, while prokaryotes lack the said genetic material-containing nucleus.
World's Largest Single Cell Organisms
Despite only consisting of one cell, there are some single cell organisms that can stretch remarkably long or grow quite big in size.
Caulerpa Taxifolia
The world's largest single cell organism is the Caulerpa taxifolia, which comes in the form of seaweed. This unicellular organism can stretch up to 10 feet in length. It is known to be quite invasive and to negatively affect other species and even humans.
Despite being an aquatic organism, the Caulerpa taxifolia is capable of surviving outside of water for 10 days. It can thrive in different kinds of habitats, including rocky outcroppings, sandy bottoms, natural meadows, and mud.
This creature is remarkably hardy. It can also reproduce from small pieces of the entire organism.
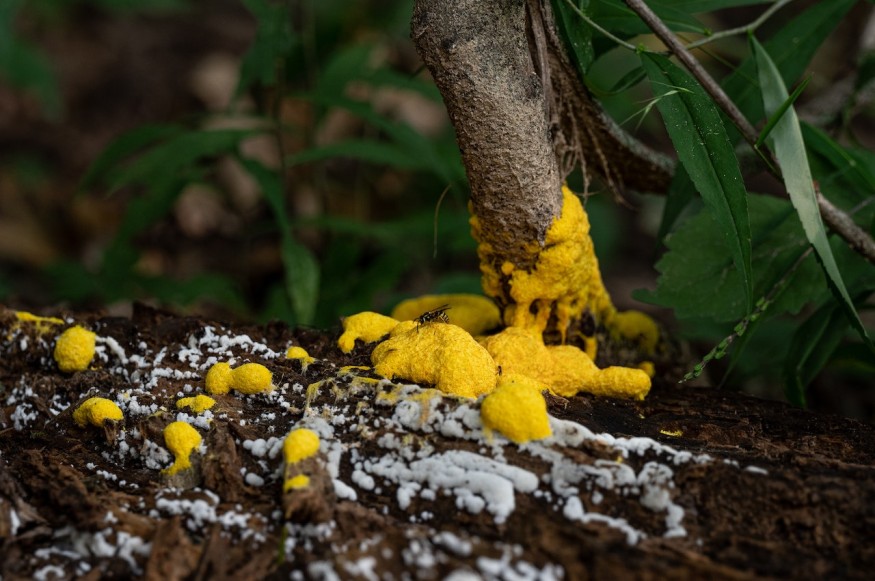
Slime Molds
Slime molds are also considered massive single cell organisms. While this is not the official name of these unicellular organisms, there are up to 900 different slime mold species. The biggest ones are capable of spanning 3 feet.
Though these creatures begin as tiny creatures that are like amoeba, they can end up merging in particular conditions. For one, plasmodial slime molds can merge together to form a single cell with several nuclei.
Syringammina Fragilissima
Syringammina fragilissima is another single celled organism, that is an amoeba by nature, that can span up to 8 inches in diameter. Its single cell expands and forms several interconnecting and hollow-branched tubes, which secrete a form of organic cement that sand and sediment particles adhere to.
Acetabularia
This algae appears to have a mushroom shape, but it can grow to a height of four inches and live in huge clusters. This single cell organism, which is also referred to as Mermaids Wineglass, is also a multinucleate organism. This means that it has several nuclei within its cell.
This unicellular organism is particularly known because it was utilized by Joachim Hammerling to reveal that genes are encoded inside the DNA of eukaryotes.
Spiculosiphon Oceana
This big eukaryote can grow up to two inches in length. Its looks and behavior is quite similar to some sponge species. Like some sponges, it creates spicule shells.
Spiculosiphon Oceana is also quite a new discovery, as it was discovered in just 2013 off the Spanish coast. The scientists behind the discovery found the species similarities with sponges quite surprising.
Check out more news and information on Biology in Science Times.
© 2026 ScienceTimes.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission. The window to the world of Science Times.