Allergy is when a person's immune system retaliates on foreign chemicals such as pollen, food, or medicine. There could be an allergy type as unexpected as cholinergic urticaria, whereby simple exposure to heat causes some hives-like skin eruptions.
What Is Cholinergic Urticaria?
Cholinergic urticaria is the disruption of red blemishes on the skin which arises when a person experiences sweating. The term "cholinergic" refers to a neurotransmitter, which is created by the parasympathetic nervous system, while "urticaria" is the medical term for hives.
Also known as heat hives or heat bumps, this kind of condition can be witnessed in a big percentage of people. Nearly 1 out of every 5 individuals develop the hives at one time of their lives.
Meanwhile, one is more likely to develop cholinergic urticaria when they have chronic hives. Other risk factors include allergic rhinitis, asthma, eczema, and excessive sweating.
Cholinergic urticaria accounts for about one in every three cases of physical urticaria. On the other hand, cholinergic urticaria occurs in about 7% of patients with chronic urticaria or those that last longer than six weeks.
These heat bumps typically rise within minutes of sweating, but they may vanish in 20 to 30 minutes. However, some individuals develop hives that last more than an hour.
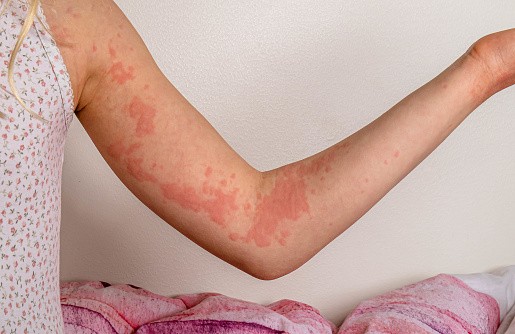
Hives typically develop on parts of the body such as the arms, the upper trunk, and the face. They form small round itchy papules that are created but often fade away within an hour. They may look like small red dots that overlie a background of redness or be joined together to form larger welts that swell.
Cholinergic urticaria presents as itchy, burning, tingling, warm hives that appear in people. The disease first appears at the age of 10-30 years.
What Causes Cholinergic Urticaria?
Health experts still do not know the exact cause for cholinergic urticaria. The theories, however, include the role of the nervous system.
When the body temperature of a person rises, he starts to sweat. In response, the nervous system of the person releases cholinergic chemicals from the nerve endings close to the surface of their skin. The cholinergic material irritates the skin of the person and causes an allergic reaction, which brings on hives and swelling.
Almost nine out of ten people experience the onset of cholinergic hives during exercise or physical exertion.
One can also be exposed to similar circumstances due to several factors. These include anxiety, fever, hot weather, hot showers, spicy foods, and stress, and applying an air- and water-tight dressing to a wound. It can also result from having drunk alcohol or being angry or upset.
A 2022 study has also determined physical factors that can result in the development of heat hives, including blocked sweat ducts or medication that inhibits the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
One further study has reported that 66% of patients that develop heat urticaria have had a histamine response against the antigens in their eccrine sweat. Very few cases have ever associated heat urticaria with exercise-induced anaphylaxis.
RELATED ARTICLE : Man Allergic to Own Semen Gets Flu-Like Symptoms; Post Orgasmic Illness Syndrome Explained
Check out more news and information on Allergies in Science Times.
© 2025 ScienceTimes.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission. The window to the world of Science Times.












