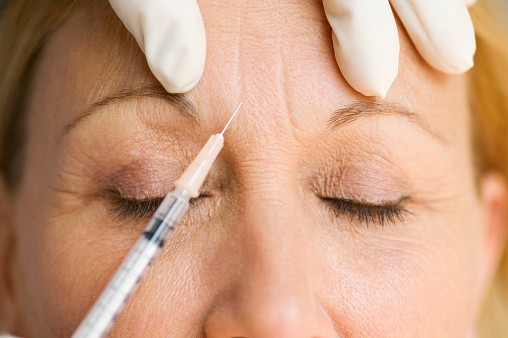
Botox represents a cosmetic medication derived from botulinum toxin, which is actually a poison.
Toxic Origin of Botox
Botox is a drug derived from an orally toxic substance owing to the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. The same toxin causes a life-threatening form of food poisoning known as botulism.
Clostridium botulinum is distributed freely in nature, in such places as soil, forests, lakes, and the gastrointestinal tracts of mammals and fish. Perceiving Clostridium botulinum bacteria and spores in food is harmless in most cases.
Difficulties are only experienced when such bacteria transform, and the cellular concentration rises. At a certain point, the bacteria begin producing Botulinum toxin, the lethal neurotoxin that causes botulism.
The bacteria that causes botulism is called Clostridium botulinum; these spores are resistant to heat and are found when there is no oxygen. There are seven distinct forms of botulinum toxin, four of which can cause human botulism.
The deadly neurotoxin can be ingested through improperly processed food in which the bacteria or the spores survive, then grow and produce toxins. Human botulism, which is largely a foodborne intoxication, can result from intestinal infection in infants, wound infections, and inhalation.
Botulinum toxin is highly toxic and is considered to be one of the deadliest substances known. It can paralyze nerve functions and can even cause respiratory and muscular paralysis.
It has been estimated by scientists that one gram of the crystalline form of the toxin can kill one million people, and a couple of kilograms could kill every human being on Earth.
Is Botox Safe?
The US Food and Drug Administration has approved Botox injection as a remedy for a number of health-related conditions. According to the American Osteopathic College of Dermatology, Botox can be appropriately used in therapeutic situations.
These include severe underarm sweating, severe neck contractions (cervical dystonia), uncontrollable blinking (blepharospasm), misaligned eyes, chronic migraine, and overactive bladder.
However, there could be some side effects such as swelling, pain, or bruising at the injected area. They can also experience headaches, flu-like symptoms, and upset stomach. Drooping eyelids are possible but on temporary grounds with injections in the face.
Botox works by weakening or even paralyzing certain muscles or blocking specific nerves that cause muscle contraction. As the treated muscles relax, so do the unwanted wrinkles and lines. The effect lasts between 3-12 months, depending on what you are treating.
Some people want Botox injections injected into various parts of their face, from around the eyes to between eyebrows, in the forehead, at the corners of the mouth, and even the cobblestone skin on the chin. The FDA, however, has approved the injections only for use around the swimmer's eyes and on the forehead.
Not everyone, however, can have Botox injected into them. Pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, and those with neurological illnesses are not allowed to have the protein injection.
Botox is actually a brand name of toxin from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum; other brands are Dysport and Xeomin. Botox is used the most because it was the first injectable botulinum toxin.
Check out more news and information on Botox in Science Times.
© 2025 ScienceTimes.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission. The window to the world of Science Times.











