Abstract: Cloud adoption and migration are critical components of modern digital transformation, enabling organizations to transition from traditional IT infrastructure to scalable, cloud-based environments. This article explores best practices for cloud migration, focusing on strategies like the 6-R framework (rehost, re-platform, repurchase, retain, retire, and refactor) to ensure alignment with strategic business objectives. It emphasizes the importance of thorough migration planning, selecting the right cloud provider, and leveraging methodologies such as DevOps and Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) to streamline the transition. Additionally, the article highlights the role of project managers in guiding successful cloud adoption by integrating technical and business considerations, utilizing cloud provider resources, and ensuring compliance with industry standards. By following these best practices, organizations can achieve enhanced agility, improved operational efficiency, and faster time to market, ultimately driving competitive advantage in an evolving digital landscape.
Keywords: Cloud Adoption, Cloud Migration, Digital Transformation, 6-R Strategy, Cloud Strategy, Project Management, Cloud Enablement, DevOps, Site Reliability Engineering (SRE), Agile Methodologies, Cloud Service Providers, Business Continuity, Cloud Security, Compliance Standards, Hybrid Cloud, IT Infrastructure, Cloud-Native Applications, Enterprise Transformation, Risk Management, Strategic Alignment
Cloud Adoption and Migration Best Practices are a set of strategies and methodologies designed to guide organizations through the transition from traditional on-premises IT infrastructure to cloud-based environments. This topic has gained significant importance in recent years as businesses increasingly recognize the potential of cloud technologies to drive digital transformation, enhance business agility, and align IT initiatives with broader strategic objectives. By adopting these best practices, organizations can achieve faster time to market, improve operational efficiency, and facilitate innovation by integrating advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning into their operations.
The evolution of cloud adoption is tightly linked to an organization's strategic goals, necessitating a collaborative approach between IT and business leaders to ensure alignment with business objectives. A critical component of this process is effective migration planning, which involves a careful assessment of both technical and non-technical factors to minimize disruption and maximize benefits. The 6-R Strategy—rehost, re-platform, repurchase, retain, retire, and refactor—provides a structured framework for organizations to evaluate and prioritize applications for migration, ensuring that each step supports the strategic goals of improved customer value, agility, and operational efficiency.
Selecting the right cloud provider is another crucial aspect of successful cloud migration. Organizations must evaluate providers based on their ability to meet specific privacy, security, performance, and compliance requirements without showing preference towards any particular vendor. The selection process should also ensure that the chosen provider can support the organization's long-term strategic objectives, facilitating a smooth transition and enabling the adoption of agile practices such as DevOps and Site Reliability Engineering (SRE).
Project managers play a pivotal role in cloud enablement by overseeing the migration process and ensuring alignment with strategic objectives. Utilizing tools and resources offered by cloud service providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud can greatly aid in managing successful migrations. These tools include training and project management resources that empower project managers to execute migration efforts efficiently, ensuring minimal disruption and optimal operational outcomes. By leveraging these best practices, organizations can navigate the complexities of cloud adoption, ultimately leading to enhanced competitiveness in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Strategic Objectives and Impact
Cloud adoption and migration are deeply intertwined with an organization's strategic objectives, serving as catalysts for digital transformation and business agility[1]. The alignment of cloud strategies with business goals is critical, as it ensures that IT initiatives support broader organizational aims, such as enhancing customer experience and improving productivity[2]. For instance, cloud adoption can facilitate faster scaling to meet traffic demands, thereby supporting strategic objectives like improving customer satisfaction and operational efficiency[3].
Aligning cloud strategies with business objectives often requires a collaborative approach, where IT and business leaders work in tandem to ensure that cloud implementations align with strategic goals[2]. This alignment can lead to significant organizational benefits, such as accelerated innovation, faster time to market, and improved agility, which are essential for staying competitive in today's fast-paced digital landscape[4]. As cloud technologies evolve, they enable organizations to adopt methodologies like DevOps and DevSecOps, further enhancing their ability to respond quickly to market demands[2].
One of the critical impacts of cloud adoption on organizational strategy is the shift towards a more agile and responsive IT infrastructure[1]. This shift not only supports faster go-to-market strategies but also facilitates the integration of emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, into business operations[4]. Moreover, cloud adoption supports the organization's broader digital transformation efforts by enabling a seamless transition from legacy systems to modern, scalable cloud environments[5].
As organizations plan their cloud migration, they must consider both technical and non-technical factors to maximize the potential benefits[6]. A phased approach to cloud migration allows businesses to evaluate carefully and select which applications and workloads to move, minimizing disruption and ensuring alignment with strategic objectives[1]. Additionally, tools and resources designed to support successful migration can play a pivotal role in managing the complexities of cloud adoption, helping organizations achieve their strategic goals more efficiently[4].
Ultimately, the successful alignment of cloud adoption with an organization's strategic objectives can drive significant improvements in operational efficiency, innovation, and market responsiveness while supporting the broader transformation of IT practices[7].
Migration Planning
Migration planning is a critical component of transitioning from an on-premises architecture to a cloud-based infrastructure. This process involves several key steps and considerations to ensure a smooth transition while minimizing disruptions to operations.
Understanding Organizational Needs
To start, it is essential for organizations to take a holistic approach when determining which applications and services to migrate to the cloud. This involves understanding the impact of migration on licensing, services, and productivity across the organization[5]. Migration can be a significant undertaking, requiring detailed planning and careful execution to maintain operational continuity during the transition[8].
The 6 Rs of Migration
One of the most effective frameworks for planning a cloud migration is the 6 Rs strategy: rehost, re-platform, repurchase, retain, retire, and refactor[9][10].
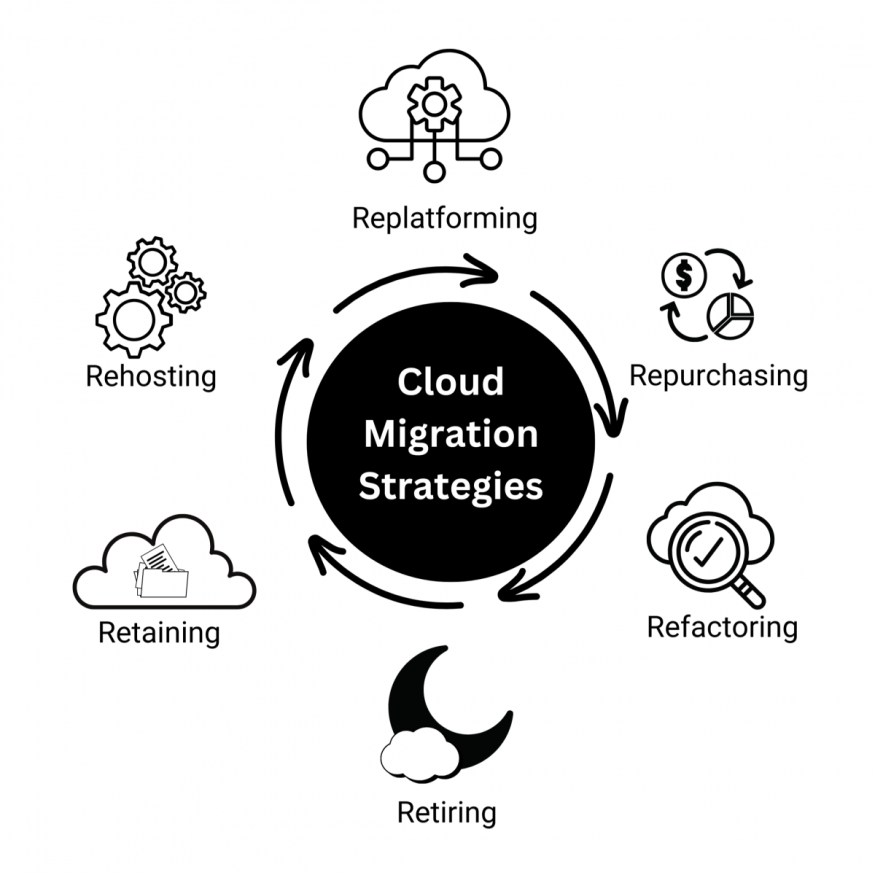
- Rehosting (or "lift and shift") is a quick solution for moving applications with minimal changes to the cloud[5][11].
- Replatforming involves optimizing applications during the migration to suit the new environment better[11].
- Repurchasing may be suitable for applications moving from customized legacy environments[9].
- Retaining allows organizations to keep certain elements on-premise, revisiting cloud migration later[9].
- Retiring involves decommissioning applications that are no longer needed[9].
- Refactoring requires significant changes to applications to leverage cloud-native features and is often chosen by organizations with rapidly evolving tech landscapes[10].
Strategic Objectives and Considerations
Cloud migration should align with an organization's strategic objectives, such as enhancing agility, improving customer value, and meeting long-term business goals[12]. As part of planning, organizations need to assess the impact of cloud adoption on IT practices and consider transitioning to more agile, DevOps-oriented processes[12].
Choosing the Right Cloud Provider
Selecting the right cloud provider is a critical decision that can influence the success of the migration. Organizations should evaluate providers based on their specific requirements and ensure that the chosen provider supports their strategic objectives without showing bias towards any particular vendor[4].
Tools and Resources
Utilizing the right tools for managing successful migration is crucial. This includes project management resources and training offered by cloud service providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. These tools can help project managers oversee migration efforts effectively, ensuring that all steps are executed efficiently and with minimal disruption to ongoing operations[10][13].
By following these guidelines and considering the 6 Rs strategy, organizations can plan and execute a successful cloud migration, paving the way for improved IT practices and faster time-to-market for new applications[10][12].
Selecting the Right Cloud Provider
Selecting the right cloud provider is a critical step in any organization's cloud adoption and migration strategy. The choice can significantly influence the performance, security, and cost-effectiveness of cloud operations. One of the primary considerations is the provider's capability to meet the organization's specific privacy, security, performance, and reliability needs, especially for sectors such as global finance, healthcare, and government that require stringent compliance standards[8]. It's essential to evaluate the technical offerings of cloud providers, including infrastructure options and regular updates, to ensure the most up-to-date technology and competitive edge[8][14].
The selection process should not only consider technical requirements but also align with the organization's business objectives and strategic goals[7]. A successful cloud adoption strategy often involves achieving competing business outcomes, such as cost reduction and enhanced customer engagement, which requires aligning financial and technical considerations to avoid misaligned motivations[7]. For instance, the cloud offers capabilities for global collaboration and nimbleness that are crucial for staying competitive[14].
Moreover, understanding the available cloud service models and frameworks is vital. This knowledge assists organizations in making informed decisions about cloud adoption, including emerging technologies like big data analytics[15]. To facilitate a smooth transition and integration, many organizations rely on automated tools and prescriptive guidance offered by cloud providers, which can support migrations, implement DevOps, and adopt Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) practices[4].
Cloud Enablement for Project Managers
Cloud enablement is a crucial aspect of modern project management, as it facilitates efficient migration and operation within cloud environments. Project managers play a pivotal role in ensuring successful cloud adoption and must be well-versed in identifying and managing project milestones effectively. A well-organized approach to milestone management can help navigate the complexities of cloud migration, ensuring alignment with both project timelines and strategic objectives[16].
To achieve successful cloud enablement, project managers must engage in early collaboration with IT and business stakeholders. This involves integrating enterprise project managers and business departments during the strategic planning stage, allowing them to articulate their objectives and ensure alignment with business goals[2]. Such engagement helps mitigate risks and streamline operations during cloud migration, fostering a culture of operational efficiency.
Training is another critical component of cloud enablement. Project managers must ensure that both IT staff and employees receive adequate training to manage and utilize cloud environments effectively[10]. This investment in time and capital for ongoing training is vital for the successful adoption of cloud technologies.
Moreover, leveraging proven combinations of cloud products and services can solve specific business problems and enhance project management strategies. Utilizing documentation and reference architectures, following best practices, and implementing solutions for common workloads on platforms like Azure can support a project's cloud strategy[6].
By focusing on strategic alignment and comprehensive training, project managers can enhance the organization's capacity to innovate, improve time to market, and boost productivity[4]. Embracing cloud technologies empowers project managers to foster an agile and responsive organizational culture, which is essential for thriving in today's dynamic digital landscape.
Tools for Managing Successful Migration
Effective management of cloud migration processes is crucial to achieving a seamless transition to cloud platforms. There are several tools and methodologies that organizations can leverage to manage successful migrations, ensuring minimal disruption to business operations.
One of the primary aspects of a successful migration is the automation of repetitive tasks. Automated tools play a pivotal role in migrating mainframe applications to the cloud, thereby reducing human error and improving efficiency[4]. Moreover, the use of automated tools can help maintain security and manage software supply chains effectively[11].
To further bolster migration efforts, organizations can adopt DevOps practices, which streamline collaboration between development and operations teams, leading to improved productivity and faster time to market[4]. Implementing DevOps processes and resources can support the effective management of migrations by enabling continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipelines and enhancing overall operational efficiency[4].
Additionally, cloud service providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud offer a suite of tools and resources to aid migration. These providers offer prescriptive guidance and reference architectures, which can be used to implement cloud adoption strategies tailored to an organization's specific needs[6]. These tools not only facilitate the migration process but also assist in optimizing the cloud environment post-migration.
Furthermore, organizations are encouraged to incorporate site reliability engineering (SRE) principles, which focus on maintaining service reliability and performance during and after migration[4]. This approach helps manage complexities that arise during migration, ensuring that applications perform reliably in the cloud environment.
By using these tools and methodologies, organizations can effectively manage their cloud migration projects, achieving enhanced operational efficiencies and supporting the strategic objectives tied to their cloud adoption journey[4][17].
Cloud Development Strategies
Cloud development strategies are essential for organizations looking to maximize the benefits of cloud adoption and migration. These strategies involve understanding the nuances of cloud environments and designing approaches that align with organizational objectives.
Understanding Cloud Infrastructure
A successful cloud development strategy begins with designing the necessary infrastructure to support applications being migrated from on-premises servers to the cloud. This involves creating a network architecture that facilitates seamless application hosting in the cloud environment[18]. Experienced cloud architects and technicians play a crucial role in this process by ensuring compatibility and consistent data backup during migration[8].
Emphasizing Agility and Innovation
Cloud environments offer unparalleled flexibility and efficiency, allowing organizations to scale services according to their needs[14]. This adaptability is pivotal for accelerating time to market and incorporating innovative technologies such as AI and machine learning into business strategies[4]. Organizations can leverage cloud services to gain a competitive advantage by rapidly deploying applications and customizing them without being bogged down by infrastructure maintenance[14].
Hybrid and Phased Approaches
While full cloud adoption is an option, many organizations opt for a hybrid approach to extend the capabilities of their existing infrastructure. This method allows businesses to operate in environments that best suit their needs while gradually increasing cloud usage as part of a phased strategy[4]. This approach minimizes disruptions and aligns with long-term digital transformation goals[1].
Cloud Enablement for Project Managers
Project managers play a vital role in cloud enablement by coordinating resources and tools necessary for successful cloud adoption. They ensure that development strategies align with organizational goals and facilitate the implementation of best practices, such as DevOps and SRE, which enhance productivity and operational efficiency[4].
Selection of Cloud Providers
Selecting the right cloud provider is crucial for successful cloud development. Organizations must evaluate providers based on their ability to meet privacy, security, and performance requirements without showing bias towards any particular vendor[8]. This careful selection process ensures that cloud services align with the organization's strategic objectives.
Challenges and Risks
Cloud adoption and migration present a variety of challenges and risks that organizations must navigate to ensure a successful transition. One of the primary challenges lies in aligning technical and business considerations. If motivations and outcomes are not aligned, organizations may face misaligned conceptions when evaluating key considerations, leading to difficulties in achieving both cost reduction and improved customer engagements simultaneously[7]. Additionally, with cloud adoption, IT departments lose centralized control over infrastructure resources, making it crucial for organizations to establish clear business guidelines and standardization to maintain secure and compliant operations[19].
Another challenge is that the migration journey is unique for each organization, as there is no one-size-fits-all plan. Each IT asset presents different cost, performance, and complexity considerations, making it essential to develop a tailored migration roadmap[10]. This roadmap should address what to move, how to move it, and the order in which components should be migrated to avoid pitfalls like data loss, downtime, and budget overruns[10].
The complexity of cloud migration can also introduce risks related to staffing and resource allocation. Organizations often have competing business motivations, which can create divides in financial investments and resource commitments to specific objectives. It is vital to scrutinize staffing plans and the critical path for shared dependencies before committing to a cloud strategy[7].
Additionally, certain workloads may not be suitable for migration due to compliance reasons or recent upgrades. In such cases, organizations must plan to revisit cloud computing at a later date, ensuring that the decision to adopt cloud services aligns with their strategic objectives and compliance requirements[13].
The decision to migrate to the cloud also requires selecting the right cloud provider and tools for managing the migration process. However, organizations must approach this choice with caution, as vendor biases should be avoided to ensure an unbiased assessment of potential benefits[7]. Properly managing these challenges and risks can lead to significant business benefits, including increased agility, improved inefficiencies, and enhanced customer experiences[1].
References
[1] Zheng, C. (2020, September 23). 6 Key Elements for a Successful Cloud Migration. IBM. https://www.ibm.com/blog/6-key-elements-for-a-successful-cloud-migration/
[2] In association with Avanade. (2020, July 15). How to align business and IT objectives for cloud adoption. CIO. https://www.cio.com/article/193701/how-to-align-business-and-it-objectives-for-cloud-adoption.html
[3] Cloud Academy. (2023, July 21). What is Cloud Migration? Strategy, Processes, Benefits & Risks. Cloud Academy. https://cloudacademy.com/blog/cloud-migration-benefits-risks/
[4] Google Cloud. (n.d.). Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing. Google Cloud. https://cloud.google.com/learn/advantages-of-cloud-computing
[5] Beacon Telecom. (n.d.). Cloud Migration Strategies: The 6 R's. Beacon Telecom. https://www.beacontelecom.com/cloud-migration-strategies-the-6-rs/
[6] Zimmergren, M., Court72, v-regandowner, Sumner, S., v-stsavell, Faurskov, J., ... & Blanchard, B. (2024, August 1). Cloud adoption scenarios. Microsoft Learn. https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cloud-adoption-framework/scenarios/
[7] Martinekuan, Zimmergren, garycentric, alexbuckgit, v-kents, Ring, W., & Blanchard, B. (2023, March 1). Build a digital transformation timeline. Microsoft Learn. https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cloud-adoption-framework/strategy/digital-transformation-timeline
[8] Erickson, J. (2023, March 16). What Is Cloud Migration? Importance, Benefits, and Strategy. Oracle. https://www.oracle.com/cloud/cloud-migration/
[9] Lucidchart. (2024). Cloud migration strategies: The 6 Rs of cloud migration. Lucidchart Blog. https://www.lucidchart.com/blog/cloud-migration-strategies-the-6-rs-of-cloud-migration
[10] Kotecha, R. (2022, September 5). Cloud Migration Strategy – The Ultimate Guide to the 6 R's. Simform. https://www.simform.com/blog/cloud-migration-strategy/
[11] QA. (2023, July 21). What is Cloud Migration? Strategy, Processes, Benefits & Risks. Cloud Academy. https://cloudacademy.com/blog/the-6-rs-of-cloud-migration/
[12] Amazon Web Services. (2024). AWS Cloud Adoption Framework (AWS CAF). Amazon Web Services. https://aws.amazon.com/cloud-adoption-framework/?tag=sciencetimes0b-20
[13] Cisco. (n.d.). What Is a Cloud Migration Strategy? Cisco. https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/cloud/what-is-a-cloud-migration-strategy.html
[14] IBM. (n.d.). What are the benefits of cloud computing? IBM. https://www.ibm.com/topics/cloud-computing-benefits
[15] Al Hadwer, A., Tavana, M., Gillis, D., & Rezania, D. (2021). A systematic review of organizational factors impacting cloud-based technology adoption using Technology-Organization-Environment framework. Digital Communications and Networks, 7(4), 478–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcan.2021.05.002
[16] PMO Team. (2024, January 15). Project Milestones: How to Identify, Establish, and Manage Them. ClickUp. https://clickup.com/blog/project-milestone-examples/
[17] Perry, Y. (2023, June 1). What is Cloud Migration? Strategy, Process and Tools. NetApp. https://bluexp.netapp.com/blog/cloud-migration-strategy-challenges-and-steps
[18] CoreStack. (n.d.). Modernizing Digital Landscape with Cloud Adoption Journey. CoreStack. https://www.corestack.io/blog/cloud-adoption-journey/
[19] Lange, K. (2022, January 25). 12 Best Practices for Cloud Adoption. BMC Software. https://www.bmc.com/blogs/cloud-adoption-best-practices/
About the Author
Sandeep Guduru is an experienced Program and Project Manager with over 14 years of expertise in cloud transformation, application modernization, and large-scale IT initiatives. He has successfully led cloud migration projects across diverse industry verticals, including financial services, healthcare, media & entertainment, and technology, working with Fortune 100 companies.
© 2025 ScienceTimes.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission. The window to the world of Science Times.












