The human brain processes visual and spatial information in fundamentally different ways than traditional 2D-based content. As Apple's Vision Pro introduces spatial computing to consumers, researchers and developers are exploring how this technology, combined with artificial intelligence, could create new possibilities for mental wellness applications.

One such experimental application leveraging this convergence is enlightenOS. enlightenOS is the brainchild of software engineer Prithiv Dev Devendran. "enlightenOS explores how AI can understand emotional states and generate appropriate therapeutic content in real time," explains Prithiv Dev. "When combined with spatial computing's ability to create presence-focused environments, it opens up new possibilities for personalized mental wellness experiences."
The vision behind enlightenOS emerged from Prithiv Dev's exploration of how emerging technologies could enhance mental wellness practices. "With advances in both AI and spatial computing, I saw an opportunity to rethink how technology could support mental health in more intuitive ways," he explains. "Rather than simply translating traditional meditation apps to VR, we could create entirely new experiences that work in harmony with how our brains naturally process immersive environments."
Available as a free download on Vision Pro's App Store, enlightenOS represents an experimental approach to gathering user insights about how AI and spatial computing might enhance mental wellness practices. "By making the app freely available, we can learn directly from users about what works and what doesn't in this new medium," notes Prithiv Dev. "These insights will be crucial for understanding how to effectively implement these technologies for mental health applications."

This integration of AI and spatial computing builds on promising research in virtual reality-based therapeutic interventions. A 2023 systematic review in the Journal of Personalized Medicine found that immersive experiences significantly enhanced therapeutic engagement, with particularly strong results in improving empathy and emotional understanding.
The technical implementation in enlightenOS focuses on what neuroscience tells us about presence and attention. "Traditional meditation apps often struggle with maintaining user presence because our brains process flat screens differently than spatial environments," Prithiv Dev notes. "By implementing precise spatial audio positioning and environmental feedback that responds to user states, we're working with rather than against natural cognitive processes."
At the core of the platform is an AI that analyzes emotional states and generates appropriate meditative guidance. This AI implementation differs from traditional approaches by creating real-time, personalized content rather than selecting from pre-recorded sessions. The system continually learns from anonymized user interaction data to refine its understanding of effective therapeutic patterns.
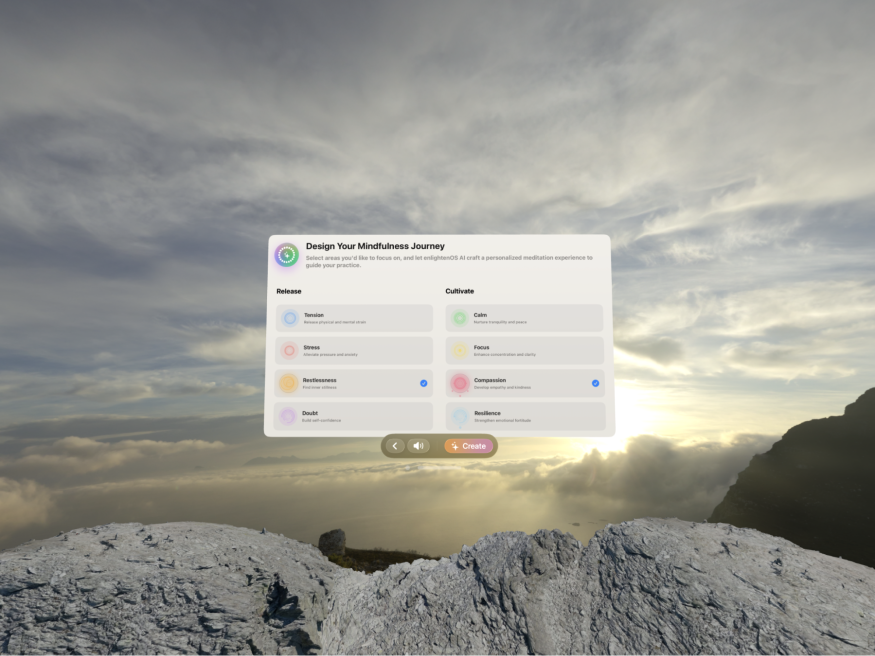
Recent research suggests this kind of personalized, adaptive approach could be particularly valuable. Studies have shown that therapeutic effectiveness often correlates with how well interventions match individual user states and preferences. The challenge has been creating systems responsive enough to adapt in real time.
"The spatial computing capabilities of Vision Pro allow us to create what we call 'presence anchors'—environmental elements that help maintain attention and emotional engagement," explains Prithiv Dev. "When combined with AI-generated content, these anchors help create a more cohesive therapeutic experience."
Early testing shows promising directions for this approach. While research specifically on AI-generated meditation content is still limited, studies on virtual reality in mental health interventions demonstrate significant potential for improving accessibility and engagement. Researchers at King's College London's Institute of Psychiatry have found that immersive environments can elicit psychological and physiological responses similar to real-world therapeutic settings.
However, important questions remain about implementing these technologies effectively. Recent papers in the field emphasize the need for rigorous evaluation frameworks and standardized approaches to measuring outcomes. As apps like enlightenOS continue to develop, the balance between innovation and clinical validation remains crucial.
Looking ahead, this convergence of spatial computing and AI could have broader implications for mental health accessibility. As these technologies evolve, the insights gained from early implementations may help shape more effective, evidence-based therapeutic tools for the future.
© 2025 ScienceTimes.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission. The window to the world of Science Times.












