NANOTECHNOLOGY
COVID-19 Vaccine Working at Room Temperature And Requires Single Shot, In The Works
Emory Chemists Invent Shape-Shifting Nanomaterial, Holding Potential for Biomedical Applications
Scientists Devise Inexpensive Yet Better ‘Pen-and-Ink’ System to Draw Flexible Circuits
Coal-Conversion Tech: Researchers Microwave Coal Powder Into Graphite

Researchers Report Tensile Elasticity in Diamonds for Microelectronics

LG Unveils New QNED TV, Using Mini LED Tech for Its Premium Display
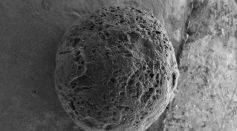
Researchers Devise A Novel Method of Producing Carbon Spheres
New Research Reveals The World of Tiny Life Forms in Da Vinci's Drawings

Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding Target Enrichment Sequencing
[LOOK] The World's Smallest 3D Printed Star Trek Spaceship and Boat
Plasma Treatments May Quickly Kill COVID-19 on Surfaces, Science Says
Scientists Discover How Coronavirus Uses "Genome Origami" to Infect and Replicate Human Cells
A New Timekeeping Theory Reconciles Einstein's Relativity and Quantum Clocks

Machine Learning Might Guide the Arrow of Time in Microscopic Processes
Most Popular

Space Tourism Future: How Commercial Space Travel Will Transform Civilian Exploration

Tree Communication Explained: How Underground Fungi Networks Connect Entire Forests

Universe Origin Revealed: Exploring the Latest Big Bang Science Theories and Discoveries

How Space Observation and the Solar Light Spectrum Make the Sun Look Different in Space Than on Earth




