PHYSICS & MATH

Google's Quantum Computer Builds First-Ever Time Crystal: Are They Now Closer to Building a Time Machine?
China Begins to Build Its Small Modular Nuclear Reactor that Will Generate a Billion kWh Every Year

How Does Piercing Work? Scientists Uncover Mechanics Behind Puncture on Soft Solids
Nobel Prize Winner Steven Weinberg Dies at 88; Here's How He Made Scientific Contributions
Generating Antimatter by High-Intensity Lasers Possible by Producing Plasma-Level Energy Similar to Neutron Star
Sound Waves Levitate Objects From Reflective Surfaces in New Method Developed by Japanese Engineers

Nuclear Explosion: Why Atomic Bombs Make Mushroom Cloud
Momentum on Planetary Scale: What Happens When Earth Suddenly Stops Spinning?

Towards Quantum Computing: Physicists Surpass Current Supercomputers With New Programmable Simulator
'Bigon Rings': Princeton Researchers Unveils Mathematics That Changes Form Based on Specific Conditions

11-Year-Old College Graduate Plans to Change Body Parts With Machines to Become "Immortal"
Isaac Newton Facts, Contributions, and Secret Mischievous Life: How He Spent His Childhood and Survived the Great Plague
Fractal Pattern in Romanesco Cauliflower Mystery Finally Discovered By Replicating It in a Common Lab Plant
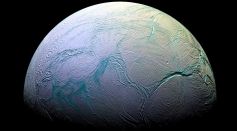
Methane Plumes on Enceladus: Could the Saturn Moon Host Life?
Most Popular

7 Breakthrough Medical Technologies Revolutionizing Healthcare in 2026

Sun Rotation Explained: How Long It Takes the Sun to Spin at Different Latitudes

Electric Car Motion Sickness: What Causes it and How to Stop It

Ocean Temperature and Winter Storms: How Sea Surface Temperatures Fuel Extreme Weather and El Niño Snowstorms




