PHYSICS & MATH
Modified MAVEN Spacecraft Found Surprising Data About the Circulation Patterns on Mars

What Careers Are Available for a Graduate With a Fire Science Degree?

Century-Old Physics Problem Solved by a Student
Whale Galaxy's Magnetic Field Observed: Astronomers Found One of the Largest Magnetic Fields
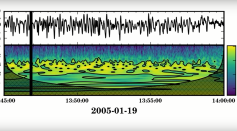
Earth's Magnetic Field Produces Music During a Solar Storm
Interstellar Comet 2I/Borisov Appears Ghostly in New Images Captured

How Do High-Pressure Temperature Sensors Work?

Jupiter's Great Red Spot is Here to Stay
Venus-Jupiter Conjunction Can Be Experienced All Throughout the Week

Astronomers Found Answers on What Lies Beyond the Solar System

Boeing Tests Starliner Capsule Launch Abort System

A Giant Leap for Mankind: The Construction of the Giant Magellan Telescope is on its Way to Completion

The Mars Helicopter is Set to Launch with the Mars 2020 Rover

Space Oven is Ready for a Test Cook-Off
Most Popular

Why Coral Reefs Are Turning White: Understanding Causes, Impact and the Science of Bleaching

Artificial Skin Breakthrough Mimics Human Sense of Touch and Temperature

Arctic Warming Reveals Climate Change Is Pushing the Region to Heat Up Four Times Faster Than Earth

Solar Flare Effects on Earth: Space Weather, Geomagnetic Storms, and Hidden Risks





