Tags: Evolution

Genomes of Roadside Weed Arabidopsis Thaliana Helps Scientist Understand Genetic Mutation

Ankylosaurs Brain CT Scan Shows Spiky Dinosaurs Are Deaf With Sluggish Movement

COVID-19 Omicron Variant May Have Evolved in Mice, Instead of Humans

If This Humans Become Extinct, Will Animals Evolve?

Black Tigers: Scientists Uncover the Secrets Behind the Genetic Mutants' Unique Stripes

Ancient Big-Headed Fish May Be the Key to Evolution, Brain Scans Show They Left Water to Invade Land

Ocean Salinity: Seawater is Less Salty Today Than First 500 Million Years of Earth
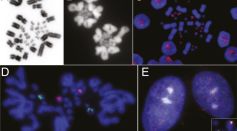
Microchromosomes Identified as Building Blocks of Every Vertebrate Animal; Junk DNA Specks More Essential than First Thought

Evolution of Mammalian Face: How Did Mammals Develop Flexible Noses That Gave Them Strong Sense of Smell?
Human Birth Canals Evolved Into a Twisted Form for a Purpose, Study Says

Newly Found Sponge-Like Structures Could Push Animal Evolution Back by Several Hundred Million Years
Modern-Looking True Crabs Discovered in Tree Amber; Study Reveals This 100 Million-Year-Old Fossil Rewrites Crustacean History

Snakes Expanded Their Dietary Plan After Dinosaur Mass Extinction 66 Million Years Ago

Evolution Explains How the Illusion of Physical Attractiveness is Wired in the Brain
Earth's Evolution: Photosynthesis Might Have Started 400 Million Years Before the Great Oxidation
Ant Social Parasitism: Plot Twists in the Origins and Evolution of These Tiny Animals Revealed
Leafy Sea Dragons: How the Majestic Marine Species Thrive Under South Australia's Underwater Biodiversity

Did Humans Have Tails? Mysterious Genetic Mutation Allegedly Made It Disappear Based on 25-Million-Year-Old Fossil

Whales Have Five Fingers Hidden in Their Flippers As Seen in Necropsy; What Is It For?

Dino-Killer Space Rock That Forms Chicxulub Crater Triggered the Evolution of Modern Snakes
Most Popular

Coral Bleaching Crisis: How Ocean Warming Threatens Marine Ecosystems Worldwide

Can EV Batteries Be Recycled? How Lithium Recovery Supports Sustainable Batteries

NASA Aurora Research Reveals How ESA Space Weather Teams Use Satellite Aurora Imaging and Ground Sensors

El Niño and La Niña Explained: How Climate Cycles Drive Extreme Global Weather Patterns





