Tags: Materials science
New Polymer Flexible Film Shields from Electromagnetic Radiation and Interference

Researchers Fabricate Novel X-Ray Photodetectors by Embedding Perovskites on Graphene
Nano-Origami Leads to Smallest ICs to Date
Vibrating 2-D Materials Could Revolutionize Electronics
Magic-Angle Twisted Graphene Could Play Host to New Phases of Matter
Scientists Establish Relationship Between Nanotube Length and Friction, To Guide Creation of Stronger Fibers
Researchers Set New Guinness World Record for Finest Woven Fabric

Ultra-Efficient, Nano-Thin Piezoelectric Materials Advance Self-Powered Electronics
Researchers Developed a “Swiss Army Knife” Catalyst from 10 Different Elements

Researchers Report Tensile Elasticity in Diamonds for Microelectronics
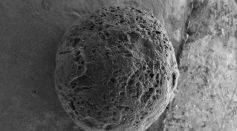
Researchers Devise A Novel Method of Producing Carbon Spheres

High-Pressure Manufacturing Improves Glass for Fiber Optic Cables
Drum Experiment Reveals Clues On Cultural Evolution
Researchers Made Biodiesel Conversion From Used Cooking Oil Easier
Self-Erasing Technology Could Prevent Counterfeiting, Tampering
Ultraclean Graphene As High Performance Magnetic Field Sensors

Ultrathin Silicon Nanoantennas Can Slow Down and Redirect Light

Scientists Capture the Moment Fluids Act Like Solids

Why Does Hair Make Your Razor Blades Dull?

New Quantum Computer Application in Materials Science
Most Popular

The Strongest Tornadoes Ever Recorded: Scientific Breakdown of Extreme Tornado Events

Can Scientists Predict Earthquakes? The Latest Advances in Seismic Forecasting Explained

How Space Affects the Human Body: Key Health Challenges Impacting the Astronauts

Photosynthesis Made Easy: Light Reactions, Calvin Cycle, and Everyday Examples




