Tags: Quantum Mechanics
European Researchers Develop New Source for Single Photons
Quantum Entanglement of Electrons Achieved Through Heat
17-year Old Maryam Tsegaye Explains Quantum Tunneling
Tunable Heisenberg Model Based on “Ultracold Atoms” Observes New Quantum Behavior
A New Timekeeping Theory Reconciles Einstein's Relativity and Quantum Clocks
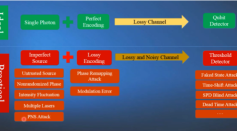
New Quantum Key Distribution Protocol Maintains Security Over Long Distances

Simple Mod Can Keep Quantum States 10,000 Times Longer
Yale Creates Error-Correcting Cat for Quantum Computers

US Reveals Potentially Impenetrable Quantum Internet

'Is This the Real World or Just a Simulation?' Quantum Musings about Experiments in 2019
Physicists Are Now Listening to the Quantum Vacuum
Quantum Computing: Trying to Scratch the Surface
Quantum Computer Time Reversal: Can It Happen?
Untangling the black hole mess
Diamond Can Generate Dynamic Unpolarized Single-Photon: New Important Stage For Quantum Computing
Large Hadron Collider Could Prove the Existence of Star Trek's Parallel Universe
Tractor Beam Tech is Now a Reality
Most Popular

Viruses vs Bacteria: Key Differences, How They Spread, and How We Treat Them

Recycling Myths vs Facts: What Actually Gets Recycled and How to Do It Right

Science-Backed Longevity Supplements: The Best Anti-Aging Vitamins for Powerful Healthy Aging Support

Space Debris and Orbital Pollution: Rising Space Junk Threats and Collision Risks Around Earth




