
5G mobile networks have become a hot topic in the digital world and pose one of the most significant challenges for telecommunications companies. Scaling this technology will not only boost data transmission and reception speeds, but also enable more devices to connect to the network simultaneously, and propel the development of numerous industries. However, achieving these advancements necessitates the creation of an infrastructure that satisfies the highest standards.
The number of users is growing
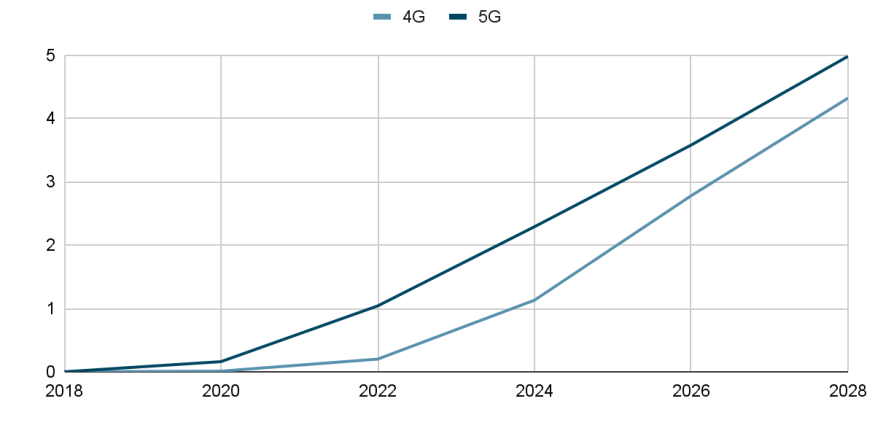
According to Ericsson, a leading telecommunications equipment manufacturer, the global number of 5G users surpassed 1 billion in 2022, with average monthly traffic increasing to 54 GB. Nearly one in three major telecommunication companies now offer 5G services to their subscribers. Projections indicate that by 2028, the number of 5G users will reach 5 billion, encompassing 85% of the global population.
Current data reveals the top three countries leading the charge in implementing this advanced communication standard in their cities are as follows:
- China (356 cities),
- USA (296 cities),
- Philippines (98 cities).
In Europe, Spain (71 cities) and Italy (65 cities) stand at the forefront of 5G adoption.
Increased business efficiency
Companies keen on automating routine processes and enhancing labor productivity are increasingly turning to 5G technology. Large businesses and manufacturing enterprises implementing Internet of Things (IoT) systems are especially diving into it. 5G offers greater bandwidth, enabling reliable connections between numerous sensors, controllers, and IoT devices. Global giants utilizing such technologies include Ford, Mercedes-Benz, and John Deere.
In the transportation sector, 5G network development plays a crucial role, particularly in supporting equipment for trucks and cars, advancing driverless car control systems, intelligent transportation systems, navigation, and accident prevention.
IoT's relevance will continue to grow in the coming years. Meticulous Research, an analytical firm, estimates that the industrial IoT market is expanding at an average rate of 16.7% annually, potentially reaching $263.4 billion by 2027. 5G, IoT, and big data analysis are collectively becoming fundamental drivers for the development of the digital economy.
The interest in 5G development extends beyond the industry. Projects are already underway to integrate 5G technology into agricultural data collection. Additionally, fintech companies can leverage 5G to bolster the security and efficiency of financial services and payments. Major media content providers like Netflix, Disney, and YouTube will also benefit from 5G infrastructure. Video producers will gain from the increased data transfer rates these networks provide, ensuring reliable connections for high-quality content. Furthermore, 5G has the potential to streamline business communications as a universal alternative to DSL and FTTH LANs.
The construction of private 5G networks could stimulate innovation within enterprises. Analytical firm, Precedence Research, estimates that the global enterprise 5G market, valued at $4.04 billion in 2022, could grow to $34.55 billion by 2030.

New technological trends are developing
Virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) technologies, which demand high network bandwidth and minimal signal delays, are among the new trends developing alongside. These technologies enable users to navigate artificial environments or interact with virtual objects in real spaces using additional equipment such as special glasses. This is achieved by creating ecosystems that integrate wearable devices, software, and cloud computing resources.
Currently, VR and AR solutions are predominantly used in the gaming industry, with the development of mobile applications and even entire VR arenas. Efforts are also being made to apply virtual reality in marketing, allowing consumers to virtually try on clothing items through mobile apps. As VR/AR technologies continue to evolve, mobile traffic will increase substantially, necessitating an infrastructure capable of providing rapid signal transmission. 5G offers significant speed improvements over 4G, with peak data transfer rates of up to 20 gigabits per second and average speeds exceeding 100 megabits per second. Undoubtedly, 5G will profoundly impact the advancement of virtual and augmented reality technologies.
Smart cities
Everyday residents are also showing interest in the expansion of 5G technology as their data consumption has increased significantly in recent years. Access control and video surveillance systems, along with remote-controlled leakage sensors, are being installed in homes. People use specialized devices to monitor their health indicators online, with sensor data sent to data centers for further processing.
Numerous services have been developed to help city authorities manage urban infrastructure and monitor activities in real-time. Sensors are integrated into monitoring systems, with collected data processed and analyzed for decision-making. This aids in regulating public transport and conserving natural resources, for example. According to analytical firm Precedence Research, the global market for smart cities was valued at $1,273.15 billion in 2022, with projections suggesting it could reach $7,162.5 billion by 2030.

To ensure the seamless operation of countless smart devices that constantly exchange information, a high-speed internet connection is necessary-something that 5G technology can provide. Building 5G networks requires a significant number of base stations and fiber connections, far exceeding the infrastructure needed for 4G and 3G networks.
Growing demand for fiber
There is a common belief that 5G may eventually replace fiber optic cable internet connections. But in fact, 5G mobile networks will have a significant impact on the wired part of the global network infrastructure. The performance of 5G networks will significantly depend on the availability of fiber and the number of fiber networks connected to cell sites. To enhance throughput, mobile operators are installing increasing numbers of base stations in designated areas, improving service quality for a growing subscriber base. Clearly, network infrastructure modernization will continue, driving demand for fiber optic products and equipment.
Currently, the fiber optics market is valued at $7.9 billion, according to analytical firm Market Research Future. By 2030, this figure could rise to $13.7 billion. The market is characterized by intense competition, with a few large companies controlling significant market shares. Major manufacturers of optical fiber and equipment are located in the United States, Japan, and China, with Southeast Asia considered the fastest-growing market. Leading players include Sumitomo Corporation and Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd. (Japan), Corning Incorporated and CommScope (USA), Zhongtian Technologies and Hengtong Optic-Electric Co., Ltd. (China). Market development focuses on creating innovative products, often achieved through various cooperation formats, mergers, and acquisitions.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to hold the largest share of the global fiber optics market in the coming years, followed by North America and Europe. By 2030, fiber usage will continue to grow across all these markets.
In conclusion, the rapid deployment of 5G networks has been a key driver of growth in the fiber optics market. Growth dynamics are influenced by factors such as the demand for improved data processing, cloud solution integration, process automation and optimization products, IoT adoption, increasing internet penetration and data transfer volumes, the need for greater network bandwidth, and growing awareness among companies about the benefits of using fiber-optic technologies.












