ENVIRONMENT & CLIMATE

World’s Oldest Mummies Dates Back 8,000 Years Ago Found in Portugal’s Mesolithic Remains
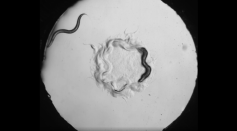
Complex Decision-Making Observed in Worms; Accounts Ability of Smaller Life Forms With Lesser Brain Cells

Venomous Palm-Sized Spider Could Survive the Cold and Potentially Spread All Over East Coast, Should You Worry?

Magnitude 7 Earthquake Could Strike Central US Within 50 Years; Population Near New Madrid Fault Line Advised to Prepare ASAP

Is Dumping Old Spacecraft in Point Nemo A Good Idea? Why Are Environmentalists Against It?

5-Foot Venomous Snake Found Curled Up Inside A Cabinet Drawer After Extreme Weather Event in Australia [Look]

14.5-Foot Enormous, Mega Star Saltwater Crocodile Known as Scarface Spotted Chilling in Queensland Creek

Farmers May Soon Be Able to Talk to Pigs Using A Breakthrough AI That Interprets Their Grunts and Oinks to Improve Animal Wellbeing

Unusual Tooth Discovered in Japanese Macaques: What is Its Significance in Human Evolution?

Endangered Dolphins Spotted in New Zealand's South Island After Conservation Department Request Sighting Reports

Megalodon Sharks Grew Larger in Cooler Waters Than Those in Warmer Areas, Study Says

Crocodile Attacks 26-Year-Old Man Taking A Bath In a River In Namibia; Why This Aggressive Reptile Assaults Humans?

Red Tail Boa Shows Artistic Side In Original Painting, Snake And Other Animals' Artwork Will Be Put on Auction at Alabama Gulf Coast Zoo

‘Cute’ Prehensile-Tailed Porcupette of Smithsonian’s National Zoo Will Tug Heart Strings! [WATCH]
Most Popular

Microplastics Are Everywhere — How Plastic Pollution Threatens Wildlife, Soil, and Water

Brain Health Aging Guide: Effective Strategies for Cognitive Decline Prevention and Lower Dementia Risk
Mitochondrial Health and Aging: How Cell Energy Drives Modern Anti-Aging Science

How Scientists Use Radio Telescopes to Search for Alien Signals Across the Universe





