Tags: Ozone layer
Polar Vortex Indicator: Aurora Borealis Reveals Rapid Ozone Layer Depletion, Affects Electricity Consumption in Northern Europe
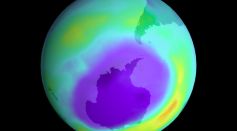
Ozone Layer Recovery Claims Might Not Be True: Controversial Study Reveals Possible Expansion of the Hole
Rocket Launches Leave Air Pollutant in Earth’s Stratosphere; NOAA Warns About Its Effects on Ozone Layer
Antarctic Ozone Hole Reaches Record Size, Threatening Further Expansion: Potential Link to Tonga Volcanic Eruption Investigated
Highest UV Index Ever: South America Set the Blazing World Record

Underestimation of One Damaging Chemical Released to the Environment Results in the Slow Repair of the Ozone Layer
Banned Chemicals That Create Holes in the Ozone Layer Are Back, Building Up at an Alarming Rate [Study]
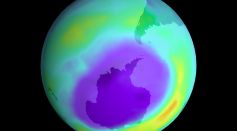
Ozone Layer Hole Over the South Pole Shrunk by 700,000 Square Miles, NASA Announces

Auroras Can Destroy Earth’s Ozone Layer [Study]

Ozone Layer's Hole Closes For Good in 2070, Scientists Claim

Scientists Develop New Metric for Earth's Ozone Layer Protection, Gauge the Impact of Emissions in the Atmosphere [Study]

New Ozone Layer Seven Times Bigger than the Antarctic Ozone
NASA’s New Climate Simulation Warns About Warming of Earth, Ozone Layer Damage; How do Flood Basalt Eruptions Contribute to These Occurrences?

Ozone Pollution Impacts Crops on East Asia, Results to 63 Billion Dollars Annual Loss
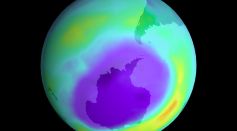
Large Hole Created in the Ozone Layer More Massive Than Antarctica Finally Set to Close This Week
Ozone Hole Forming Each Year Over South Pole Presently Larger Than Entire Antarctica; Report Says It's Due to Depletion
Nuclear Warfare Smokes Can Block Ultraviolet Lights from the Sun, 15-Year Thinning of Ozone Layer
Montreal Protocol Unexpectedly Saved Earth From Significant Climate Change; What Does It Mean?
Megaconstellation Satellites Reentering Puts a Hole in Ozone Layer, Increases Atmosphere Pollution, and Uncontrolled Geoengineering
Ozone Layer May Fully Recover Despite Holes Over the North & South Poles
Most Popular

Largest Known Volcanic Aquifer Discovered Beneath Oregon's Cascades

New 'Supergiant' Sea Bug Found in South China Sea, Named After Darth Vader

Mediterranean Sea Was Refilled by a Catastrophic Flood Millions of Years Ago

Mysterious Cosmic Waves That Sound Like Birds Detected in Unexpected Space Region





