evolution
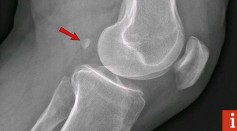
Fabelle: Extinct Bone in the Human Body Coming Back

New Study Shows that Life on Earth Began in a Shallow Pond, Not in the Ocean

Scientists Have Just Discovered Homo Apriliensis, the Hominid Species with a Tail

Charles Darwin’s Mystery Animal: Solved!

Fossils Of Homo Sapiens From Morocco May Change Dates Of Darwin's Theory of Evolution

Humans First Evolve In Europe Not In Africa, Fossils Prove
Scientists Use 3D Printed Eggs to Study the Art of Deception among Birds

Gene Sequencing and Color Mapping Reveal Potential New Species among Flamboyant Panther Chameleons
Ancient DNA Shows Dogs Split from Wolves Much Earlier than Previous Estimates
Yale Traces the Origins of all Snakes
Up From the Depths: The First Warm-Blooded Fish
The Trap-Jaws’ Mighty Mandibles Propel Them from Danger

Macaques Prove Quite Handy with a Hammer
Embryological Manipulation Reveals Chicks Can Have Prehistoric Looks
Most Popular

How a Plant-Based Diet Can Protect Against Breast Cancer: Insights from Nutrition Research

Study Reveals High Turnover in Scientific Research Careers: What This Means for Future Scientists

How Technology Is Changing the Real Estate Industry?

Practical Steps to Future-Proof Your Money to Create Financial Security






