Exoplanets

'Mini-Neptune' Exoplanets With Puffy Atmospheres are Transforming Into Super-Earths; How Is This Possible?

Super Neptune Exoplanet Has Water Vapor In Its Atmosphere Providing Clues on the Gas Giants in the Solar System
ExoMiner Deep Neural Network Finds 301 New Exoplanets Added to the Total Count of NASA's Kepler Mission
NASA Discovered "Hot Jupiter" Exoplanet, Bigger But Less Massive Than Solar System's Largest Planet
Astronomers Detected Clouds on Distant Exoplanet WASP-127b, Revealing the Upper Structure of Its Atmosphere
Earth's Atmosphere Seems to be 'Unique', No Other Exoplanets Could Compare
Gaseous Planets Orbiting Bright Star Discovered: Citizen Scientists Finds Exoplanets With Sizes Like Neptune and Saturn

Researchers Discover Jupiter-Like Exoplanet that has Complex Weather System
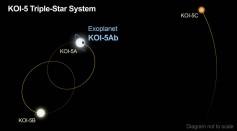
Kepler Finds Triple-Star System With a Skewed Configuration

Stars May Be Responsible for Inhabitable Exoplanets

X-Ray Data Reveals First Planet Candidate From Another Galaxy
NASA Missions Find Survivor Planet Orbiting Remains of Dead Star

New Study Finds at Least 45 Planets With Qualities Similar to Earth

An AI Algorithm Was Used to Identify Exoplanets
Most Popular

How Technology Is Changing the Real Estate Industry?

Nikolay Karpenko Biography, Photo, Career, Accomplishments

How a Plant-Based Diet Can Protect Against Breast Cancer: Insights from Nutrition Research

The Role of AI in the Next Generation of Logistics: Insights from Tobias Waldhecker






