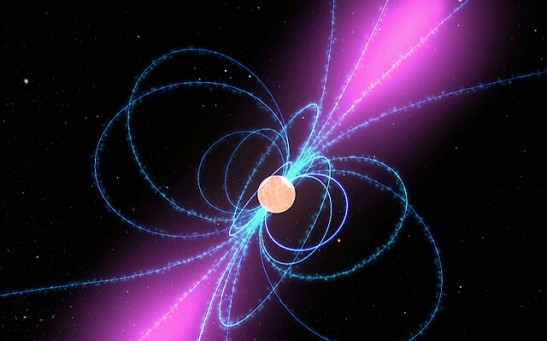
Magnetic Fields

Moon Used To Share Magnetic Field With Earth, Protecting Our Atmosphere
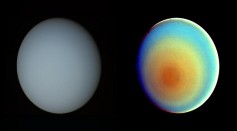
Uranus, a Weird Planet, Has a Weird Magnetic Field
NASA’s New MMS Study Revealed Dance Of The Electrons In Earth’s Magnetosphere

Scientists Discovered Source That Speeds Up Magnetic Reconnection
Can Magnetism Bend Heat And Sound? Study Reveals A New Dimension to Magnetic Fields
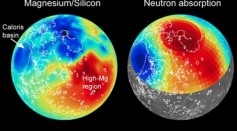
New NASA Maps Reveal Secrets of Mercury

Researchers Reveal Method for Magnetic Field Calculation of Exoplanets

Earth's Rapidly Shifting Magnetic Field Could Impact Your Health
Most Popular

How Technology Is Changing the Real Estate Industry?
AI Revolution in Medical Education: Transforming How Healthcare Professionals Learn

Nikolay Karpenko Biography, Photo, Career, Accomplishments

Zombie Star Set to Light Up Night Sky: Blaze Star Could Erupt Soon