medicine
New Treatment for Migraines Could Bring Much Needed Relief
Leprosy Rears its Ancient Head with New Cases in Florida
VIDEO—The LEAP Trial and How Researchers Revealed No Threat in Allergens
When It Comes to Allergens—Is It Best to Stay Away?
Researchers Reveal That Killer ‘Bourbon Virus’ is Of the Rare Thogotovirus Genus
How Arachnids May Reveal Looming New Threats to American Public Health—Bourbon Virus
Health Experts Reveal Importance of a Low-Fat Diet, and Urge Americans to Splurge on Veggies Instead

Apple May Be Tabling Health-Monitoring from its Watch, But It’ll Still Pack a Punch
Superbug Breaks Out at UCLA Medical Center, Causing Concern for Safety of Endoscopic Procedures

When It Comes to Pandemics and Outbreaks, Could Climate Change Be to Blame?

When It Comes to Pandemics and Outbreaks, Could Climate Change Be to Blame?
Duchess of Cambridge, Kate Middleton Marks the Start of Children’s Mental Health Week with a Call to Action
Could New HIV Strain Cross the Atlantic? Fears of the Spread of Aggressive HIV from Cuba
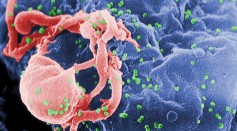
New HIV Strain in Cuba Has Researchers Rushing to Stop Fast Progression of AIDS
Most Popular

How Technology Is Changing the Real Estate Industry?
AI Revolution in Medical Education: Transforming How Healthcare Professionals Learn

Nikolay Karpenko Biography, Photo, Career, Accomplishments

Zombie Star Set to Light Up Night Sky: Blaze Star Could Erupt Soon





