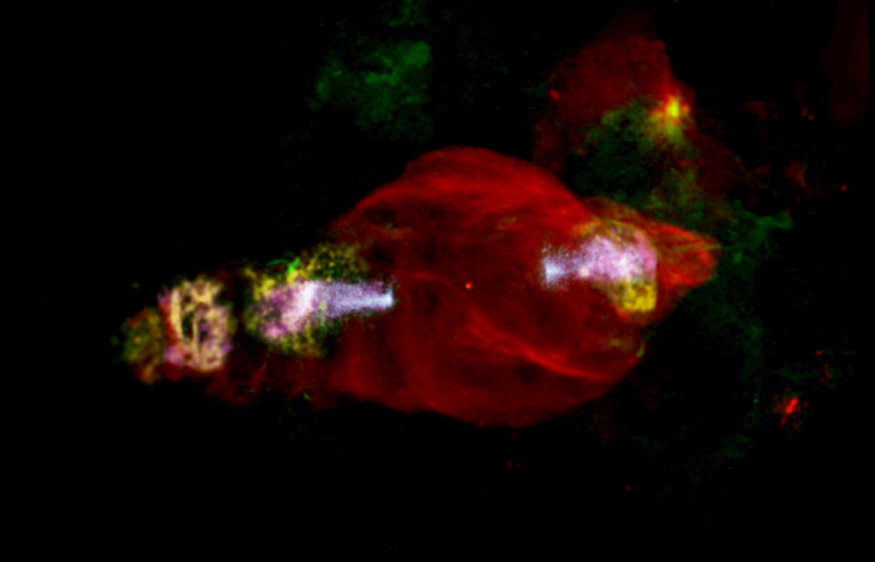
The Manatee Nebula, also known as W50, was photographed by the European Space Agency's XMM-Newton X-ray observatory, revealing the location of exceptional particle acceleration in its "head."
ESA's X-Ray Observatory Finds Odd Creature's Head
SciTechDaily said Manatee Nebula, also known as Westerhout 50, is a sizable supernova remnant left behind after a massive star's explosion 30,000 years ago. It is now one of the biggest known features of its type, measuring four full moons in size.
It is even rarer for a supernova remnant since it has a black hole at its center. The black hole, known as SS 433, releases strong jets of particles that move through the gaseous shells at speeds that are almost a fourth of the speed of light. It then took the shape of a double-loped shape.
The Manatee's head X-ray jet's particle acceleration zone was precisely located thanks to the ESA's XMM Newton. It begins at a distance of around 100 light-years from the microquasar and stretches out for about 300 light-years.
"Thanks to the new XMM-Newton data, supplemented with NuSTAR and Chandra data, we believe the particles are getting accelerated to very high energies in the head of the Manatee through an unusually energetic particle acceleration process," said principal investigator Samar Safi-Harb of the University of Manitoba in Canada per Devdiscourse.
Safi-Harb added there is a good chance that the black hole outflow made it there and has been reenergized there, maybe by shock waves in the spreading gas clouds and stronger magnetic fields.
The data from NuSTAR and Chandra were also used to support the mission. It has improved the researchers' understanding of the Manatee Nebula. They now think the particles are accelerated to abnormally high energy by a particle acceleration mechanism. Additionally, they believe that the gas cloud shock waves and stronger magnetic fields are how the black hole arrived at its location.
The study, "Hard X-ray emission from the eastern jet of SS 433 powering the W50 'Manatee' nebula: Evidence for particle re-acceleration," will be published in the Astrophysical Journal.
According to ESA, the nebula will work as a close laboratory for scientists today as they investigate different astrophysical processes connected to the outflows of several galactic and extragalactic sources.
ESA will continue research using the upcoming Athena X-ray observatory. It will make providing even more delicate information regarding the Manatee's internal workings easier.
Where The Odd Creature's Head Is Located
When the High-Altitude Water Cherenkov Observatory revealed the presence of highly energetic particles at Westerhout 50 in 2018, SciNews mentioned that the discovery attracted attention. However, it was unable to determine where within the supernova remnant the particles were originating.
Westerhout 50, also known as W50 or SNR G039.7-02.0, is a star in the constellation of Aquila that is situated about 5,500 parsecs (18,000 light-years) from Earth.
With a diameter of more than 200 × 100 parsecs (652 x 326 light-years), it is one of the biggest supernova remnants in our galaxy that is currently known.
When a massive star burst around 30,000 years ago, its gas shells were thrown across the sky and became Westerhout 50.
RELATED ARTICLE : Chandra Telescope Captures Intermediate Black Holes in Star-Filled Galaxies, Explains How They Obtain Absurd Sizes
Check out more news and information on Space in Science Times.












