ENVIRONMENT & CLIMATE
Geothermal Activity Under Antarctic Ice Sheet Bring Thwaites Glacier on Brink of Collapse Due to Excessive Melting

Four Storms, Wildfires Over North American Continent Captured Via Satellite Imaging
Why is White Clover Poisonous? Study Claims Its Chemical Defense Mechanism Resulted From Hybridization

Antarctic Ice Sheet's Rising Sea Levels Could Be 'Countered' by Snowfall Induced Through Warming Ocean of Northern Hemisphere

Hottest Month in History To Bring Drought and Fire Clouds in Future Summers

Two Female Sharks Reproduce Offspring; Recorded as First Case of Asexual Reproduction in Italy
Babbling Bats: Like an Infant, These Animal Species Babble to Get Their Parents' Attention

SINAI Technologies, Decarbonization Startup, Raises $10M in Seed Funding Round
Earth Destruction: Is This Really Possible? Black Holes, Volcanoes, Robotics May Negatively Impact the Planet in the Future
Cells Discovered in Corals, Sea Anemones, Engulfing Bacteria; A Discovery Potential for Better Marine Health Assessment
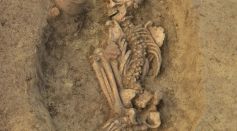
Archaeogenetics in Croatia's Neolithic, Bronze Age Possible Missing Piece of European Ancestry

Measuring Firebrands: New 'Emberometer' Uses 3D Imaging Techniques To Assess Wildfire Threats
Red Junglefowl Experiment Reveals Genetic Expression and Cognitive Enrichment Influence on Impulsivity
[Watch] Alaskan Bear Wandering Around With Up to 9 Meters Long Tapeworms Hanging From Their Butts
Most Popular

NASA Reveals an Astronaut Was Medically Evacuated From the ISS for the First Time After a Non-Emergency Health Scare

How the Immune System Fights Diseases: Antibodies, Vaccines & Lasting Protection

Sun Reaches Solar Maximum: What the Intensifying 11-Year Solar Cycle Means for Earth

Ancient Interbreeding Between Neanderthals and Modern Humans Revealed




