
Olive Marie

Experts Explain Reason UK Variant COVID-19 Could Be More Deadly

Engineers Devise Machines to Remove CO2 from the Air, Could Potentially Stop Climate Change

Primates Could Probably Talk If They Exerted Any Effort—Biologists

AstraZeneca Counters German Reports Its COVID-19 Vaccine is Only 8% Efficient for People Aged Over 65

How Hug Affect Our Mental Health Especially in This Time of Pandemic
Researchers Discover 'Exquisitely' Preserved Skull of a Dinosaur that Lived Over 70 Million Years Ago
Researchers Predict Increase in Cancer Cases That Need Surgery

About 25% of All Bee Species ‘Unseen’ Since 1990
EU Pressuring AstraZeneca for its Promised Delivery of COVID-19 Vaccines

Man’s Best Friend No More: Does a Dog Now Belong To a Woman?
Medical Experts Explain That Immunotherapy Can Treat Some Types of Cancers
Impulsive Risk-Taking Associated with Losing Visceral Fat

Pesticide Is The Reason Bees Are Not Getting Adequate Sleep
For Some People, COVID-19 Might Spread Through Eating
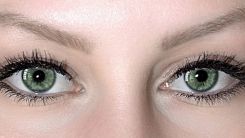
Believing is Seeing: Discovering the Link Between What We Expect to See and What Our Brain Tells Us
Blue Origin Announces It’s Getting ‘Really Close’ to Flying Humans
New Data Shows UK Variant May Be 30% More Fatal

Scientists Explain the Neurobiology of Thirst
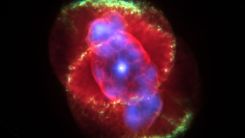
Study Explains the Reason for Two White Dwarfs’ Collision
Water Ice Mapped Across Northern Part of Ganymede, the Largest Moon in the Solar System
NASA’s Perseverance Rover Set to Land on Mars in Less Than a Month

Mask Said To Deactivate Different Coronavirus Types in 2 Hours

Are You a Frequent Eater of Potato Chips? Here Are 5 of the Health Conditions You Should Watch Out For
What’s Causing the Tilt on Saturn’s Rotation Axis?

SpaceX Launches 17th Batch of Starlink Satellites, First for 2021

Scientists Develop Pioneering Biomarker To Predict Depression and Bipolar Disorder

Pfizer-BioNTech Vaccine Likely To Work Against New COVID-19 Strain In UK

NASA Astronauts To Install High-Speed Satellite Link for Enhanced Transmission of Data Between Land and the Station

Chemist Explains How Oil is Turned into Plastic
Most Popular

Microplastics Are Everywhere — How Plastic Pollution Threatens Wildlife, Soil, and Water

How Scientists Use Radio Telescopes to Search for Alien Signals Across the Universe

How Climate Change Amplifies Natural Disasters: Extreme Weather and Global Warming Impact

Climate Change Effect on Wildlife: How Shifting Habitats Are Transforming Animal Migration Patterns




