Tags: Radiation

UV Radiation May Have Been Involved in the End-Permian Mass Extinction Event, Fossil Analysis Reveals

Supermassive Black Hole Gorging on a Star Launches Leftover via 'Relativistic Jets' Toward Earth

Destructive Solar Storms May Not be Responsible for Radiation Shadows on Earth Trees

Conan the Bacterium Could Survive for 280 Million Years on Mars Beneath the Surface, Study Claims

Will Cockroaches Survive a Nuclear War? Previously Assumed Extinct Species Found Again, Proving Their Longevity and Survivability
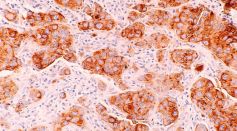
Treatment of Precancerous Lesions in Breast Duct Can Eliminate All Signs of Early Breast Cancer

Space Bubbles Might Work as Massive Sunblock of Earth from Radiations to Mitigate Global Warming
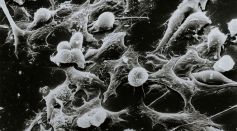
Immunotherapy Drug Anti-Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 Dostarlimb Has 100% Efficacy Rate Against A Subset of Rectal Cancer [Study]

Scientists Discover New Effect in 2D Conductive Systems Promising Better Performance of Terahertz Detectors
Electromagnetic Radiation Effect from Tech Devices Draw Fears Among People; How Does Snake Oil Help Alleviate Such Apprehensions?

Reverse Solar Panel Generates Electricity Without Sunlight by Emitting Heat to Cold Night Skies

Repeatedly Exploding Stat Produces Gamma Ray, What Is Stellar Vampirism?

Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant's Data in Jeopardy After Remote Systems Went Missing

Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant Spiked 20 Times Its Original Radiation After Captured by Russian Military

How Can a Giant Laser Help Lessen Astronaut's Exposure to Radiation? Gigantic Space Object Reduces Mars Mission from 10 Months to 45 Days Long
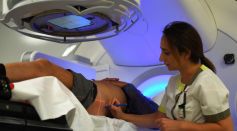
New Cancer Treatment May End Chemotherapy and Radiation, How Does It Work?

‘Anti-5G’ Radiation Necklaces Are Dangerously Radioactive, Experts Warn
Low-Dose CT Scan Can Accurately Diagnose Appendicitis, Decrease Radiation Exposure

Genius Russian Child Claims He is From Mars, Will Save Humanity from Nuclear Destruction; Who Is Boriska Kipriyanovich?
Spatial Learning Impairment Observed from Deep Space Radiation-Exposed Mice, Affects Male Subjects Than Female
Most Popular

Space Tourism Future: How Commercial Space Travel Will Transform Civilian Exploration

Universe Origin Revealed: Exploring the Latest Big Bang Science Theories and Discoveries

Big Bang Physics and Cosmology: Can Science Really Explain the Origins of the Universe?

Tree Communication Explained: How Underground Fungi Networks Connect Entire Forests





