TECH & INNOVATION
A Decoder to Turn Brain Activity Into Speech
African Teen Builds Windmills from Junk and Supplies His Village with Electricity
Longer Lasting Lithium Batteries Are Here
OSCAR: The Space Janitor
Taiwan Introduces New Formulation of Reinforced Concrete
Scientists Used Bacteria to Make Synthetic Mother-of-Pearl
A Coding Language for the Blind and Visually Impaired
EndoPil: The Holy Grail in Weight-Control?
A No-Engine, No-Fuel Aircraft
Technological DNA Can Be Stolen Via Phones
The Incredible, Edible… Straw?
Drones Approved to Make US Home Deliveries
WhatsApp is Used as a Tool for Antisocial Hatred in India
Colussus: The Firefighting Robot
Most Popular
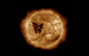
Butterfly Shaped Hole On The Sun Appears: What Is It, How Much Bigger Than The Earth Is It, And How Will It Affect Us?

NASA to Launch This Month Three Spacecraft That Could Save Your Next Flight or Bank Transfer

Tesla Cybertruck Crashes Anti-ICE Protests in LA, Becomes Unlikely Symbol of Trump Controversy

Elon Musk Claims Tesla Robotaxi Will Hit Streets This Month: 'Most Important Product' Yet




